「大量のWordやExcelファイルを、一つずつPDFに変換するのが面倒…」
こんな風に感じたことはありませんか? 私の職場でも、こうした手作業に多くの時間が割かれていました。
この記事では、そんな悩みを解決するために、Windows標準のPowerShellだけで作った「Officeファイル一括PDF変換ツール」について、その背景から具体的な実装までをご紹介します。
背景:なぜPowerShellを選んだのか
ツールの開発にあたり、まず考えたのが「誰でも簡単に使えること」でした。
Pythonなどの言語で高機能なツールを作ることも可能ですが、それを使うためには各PCに実行環境をインストールする必要があります。しかし、会社のPCに自由にソフトをインストールするのは、セキュリティポリシー上、難しい場合が多いですよね。
そこで白羽の矢が立ったのが、Windowsに標準搭載されているPowerShellです。
- インストール不要: 追加の環境構築なしで、どのWindows PCでも動きます。
- Officeとの親和性: 標準機能でWordやExcelを直接操作できます。
- GUIも作れる: 見た目も分かりやすいGUIアプリケーションを構築可能です。
「配布が簡単で、誰でもすぐに使える」という、情シス子飼いのツールとして理想的な条件を満たしていたのが、PowerShellを選んだ決め手でした。
完成したツールの紹介
こちらが完成したツールです。
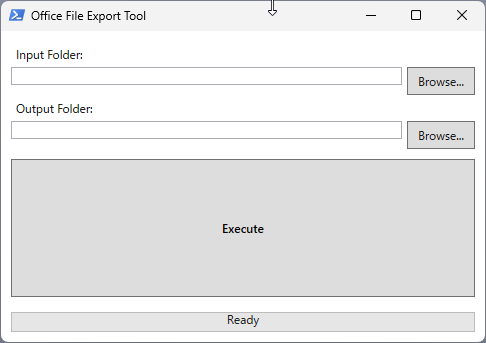
主な機能
- フォルダを指定するだけの簡単操作: 変換したいファイルが入ったフォルダと、PDFの保存先フォルダを選ぶだけ。
- サブフォルダも自動検索: 指定したフォルダの中にあるファイルを、サブフォルダまで含めてすべて探し出し、一括で変換します。
- リアルタイム進捗表示: 今どのファイルを処理しているのか、全体で何パーセント完了したのかが、ひと目で分かります。
使い方
1. ファイルの準備
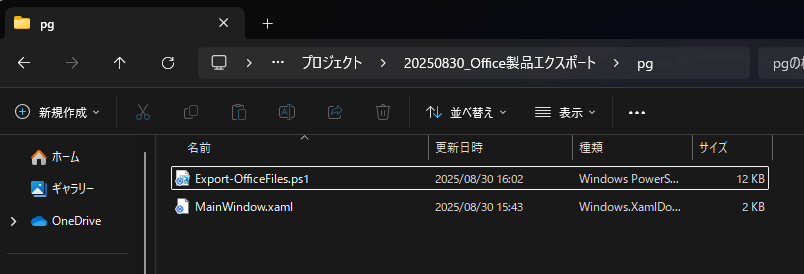
まず、以下の2つのファイルをダウンロードし、同じフォルダに保存してください。
Export-OfficeFiles.ps1(PowerShellスクリプト本体)MainWindow.xaml(GUIの定義ファイル)
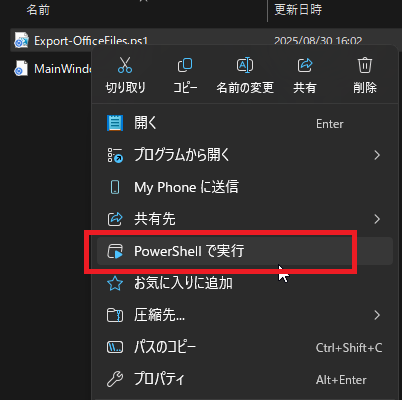
2. スクリプトの実行
Export-OfficeFiles.ps1 ファイルを右クリックし、メニューから「PowerShell で実行」を選択します。
もしセキュリティ警告が表示された場合は、「開く」をクリックしてください。
3. フォルダの選択
ツールが起動したら、まず「Input Folder」の横にある「Browse…」ボタンをクリックし、変換したいOfficeファイルが保存されているフォルダを選択します。
次に、「Output Folder」の横にある「Browse…」ボタンをクリックし、変換後のPDFファイルを保存したいフォルダを選択します。
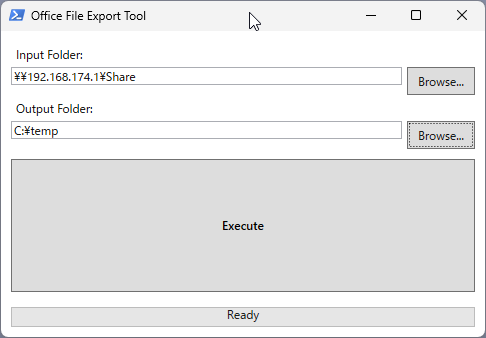
4. 変換の実行
フォルダの選択が完了したら、「Execute」ボタンをクリックします。
変換処理が開始され、プログレスバーが進み始めます。処理が完了すると、画面下部のステータス表示が “Processing completed successfully.” に変わります。
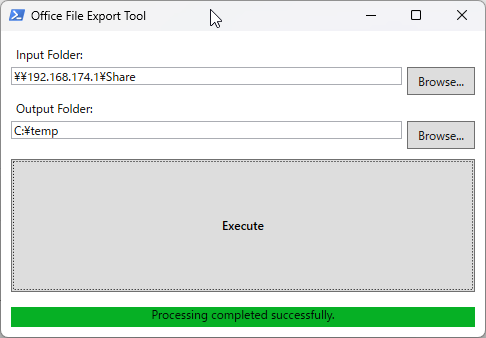
以上で、指定した出力先フォルダにPDFファイルが作成されているはずです。
実装のポイント解説
このツールは、UI(見た目)を定義するMainWindow.xamlと、実際の処理を記述するExport-OfficeFiles.ps1の2つのファイルで構成されています。
1. Officeを操作する心臓部「COMオブジェクト」
PowerShellからWordやExcelを操作する核となるのが「COMオブジェクト」です。以下のように記述することで、PowerShellのスクリプトからPowerPointを起動し、ファイルをPDF形式で保存できます。
function Convert-PowerPointToPdf {
param($sourcePath, $destinationPath)
$powerpoint = $null
try {
# PowerPointのプロセスをバックグラウンドで起動
$powerpoint = New-Object -ComObject PowerPoint.Application
# 指定されたファイルを開く
$presentation = $powerpoint.Presentations.Open($sourcePath, $true, $false, $false)
# PDF形式(定数:32)で名前を付けて保存
$presentation.SaveAs($destinationPath, 32)
$presentation.Close()
}
finally {
# 処理が終わったら、プロセスを確実に終了させる
if ($powerpoint) {
$powerpoint.Quit()
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($powerpoint) | Out-Null
}
}
}try-finallyブロックを使っているのがポイントです。これにより、変換中に万が一エラーが発生しても、PowerPointのプロセスがPCに残り続けるのを防いでいます。
2. モダンなフォルダ選択ダイアログの実装
当初、PowerShell標準のフォルダ選択ダイアログはUIが古く、少し使いにくいものでした。
そこで、WindowsのAPIを直接呼び出すC#コードをPowerShellに組み込むことで、以下のようなモダンなUIを実現しました。
function Select-FolderDialog {
param (
[string]$Title = "Select Folder"
)
# C#コードをヒアドキュメントで定義
$code = @"
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
public class FolderSelectDialog
{
// (中略) Windows APIを呼び出すための複雑な定義
}
"@
# 定義したC#コードをPowerShell内でコンパイルして使用可能にする
if (-not ("FolderSelectDialog" -as [type])) {
Add-Type -TypeDefinition $code -ReferencedAssemblies System.Windows.Forms
}
# 作成したクラスのインスタンスを生成してダイアログを表示
$dialog = New-Object FolderSelectDialog
$dialog.Title = $Title
if ($dialog.ShowDialog()) {
return $dialog.FileName
}
return $null
}少し複雑ですが、このおまじないを追加するだけで、ツールの使い勝手が格段に向上します。
プログラム全体
このツールは、UI(見た目)を定義するMainWindow.xamlと、実際の処理を記述するExport-OfficeFiles.ps1の2つのファイルで構成されています。
MainWindow.xaml
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Office File Export Tool" Height="350" Width="500">
<Grid Margin="10">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Label Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Content="Input Folder:" />
<TextBox x:Name="InputFolderPath" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Margin="0,0,5,10" IsReadOnly="True" />
<Button x:Name="BrowseInputFolderButton" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Content="Browse..." Padding="10,2" />
<Label Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" Content="Output Folder:" />
<TextBox x:Name="OutputFolderPath" Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="0" Margin="0,0,5,10" IsReadOnly="True" />
<Button x:Name="BrowseOutputFolderButton" Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="1" Content="Browse..." Padding="10,2" />
<Button x:Name="ExecuteButton" Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" Content="Execute" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,10" />
<ProgressBar x:Name="ProgressBar" Grid.Row="5" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" Height="20" Margin="0,5,0,0" />
<TextBlock x:Name="StatusText" Grid.Row="5" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" Text="Ready" HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" />
</Grid>
</Window>Export-OfficeFiles.ps1
# Set script encoding to UTF-8
[System.Console]::OutputEncoding = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8
$PSDefaultParameterValues['*:Encoding'] = 'utf8'
# Load assemblies
Add-Type -AssemblyName PresentationFramework, System.Windows.Forms, WindowsBase
# Path to the XAML file
$xamlPath = Join-Path $PSScriptRoot "MainWindow.xaml"
# Load XAML file and create the window
try {
$xaml = [xml](Get-Content -Path $xamlPath -Raw)
$reader = (New-Object System.Xml.XmlNodeReader $xaml)
$Window = [System.Windows.Markup.XamlReader]::Load($reader)
}
catch {
Write-Error "Failed to load XAML file: $($_.Exception.Message)"
exit
}
# Get controls from XAML
$InputFolderPath = $Window.FindName("InputFolderPath")
$BrowseInputFolderButton = $Window.FindName("BrowseInputFolderButton")
$OutputFolderPath = $Window.FindName("OutputFolderPath")
$BrowseOutputFolderButton = $Window.FindName("BrowseOutputFolderButton")
$ExecuteButton = $Window.FindName("ExecuteButton")
$ProgressBar = $Window.FindName("ProgressBar")
$StatusText = $Window.FindName("StatusText")
# Function to display a modern folder selection dialog
function Select-FolderDialog {
param (
[string]$Title = "Select Folder"
)
$code = @"
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
public class FolderSelectDialog
{
public string InitialDirectory { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string FileName { get; set; }
public FolderSelectDialog()
{
FileName = "";
}
public bool ShowDialog()
{
IFileOpenDialog dialog = (IFileOpenDialog)new FileOpenDialog();
try
{
dialog.SetOptions(FOS.FOS_PICKFOLDERS | FOS.FOS_FORCEFILESYSTEM);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(InitialDirectory))
{
IShellItem item;
if (SHCreateItemFromParsingName(InitialDirectory, IntPtr.Zero, typeof(IShellItem).GUID, out item) == 0)
{
dialog.SetFolder(item);
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(item);
}
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(Title))
{
dialog.SetTitle(Title);
}
if (dialog.Show(IntPtr.Zero) == 0)
{
IShellItem item;
if (dialog.GetResult(out item) == 0)
{
IntPtr pszString;
if (item.GetDisplayName(SIGDN.SIGDN_FILESYSPATH, out pszString) == 0)
{
if (pszString != IntPtr.Zero)
{
try
{
FileName = Marshal.PtrToStringAuto(pszString);
return true;
}
finally
{
Marshal.FreeCoTaskMem(pszString);
}
}
}
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(item);
}
}
}
finally
{
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(dialog);
}
return false;
}
[DllImport("shell32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Unicode)]
private static extern int SHCreateItemFromParsingName(string pszPath, IntPtr pbc, [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStruct)] Guid riid, out IShellItem ppv);
}
[ComImport, Guid("DC1C5A9C-E88A-4dde-A5A1-60F82A20AEF7")]
internal class FileOpenDialog { }
[ComImport, Guid("42f85136-db7e-439c-85f1-e4075d135fc8"), InterfaceType(ComInterfaceType.InterfaceIsIUnknown)]
internal interface IFileOpenDialog
{
[PreserveSig] int Show(IntPtr parent);
void SetFileTypes(uint cFileTypes, [In] IntPtr rgFilterSpec);
void SetFileTypeIndex([In] uint iFileType);
void GetFileTypeIndex(out uint piFileType);
void Advise(IntPtr pfde, out uint pdwCookie);
void Unadvise(uint dwCookie);
void SetOptions([In] FOS fos);
void GetOptions(out FOS pfos);
void SetDefaultFolder(IShellItem psi);
void SetFolder(IShellItem psi);
void GetFolder(out IShellItem ppsi);
void GetCurrentSelection(out IShellItem ppsi);
void SetFileName([In, MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] string pszName);
void GetFileName([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] out string pszName);
void SetTitle([In, MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] string pszTitle);
void SetOkButtonLabel([In, MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] string pszText);
void SetFileNameLabel([In, MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] string pszLabel);
[PreserveSig]
int GetResult(out IShellItem ppsi);
void AddPlace(IShellItem psi, int alignment);
void SetDefaultExtension([In, MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] string pszDefaultExtension);
void GetDefaultExtension([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPWStr)] out string pszDefaultExtension);
void Close(int hr);
void SetClientGuid();
void ClearClientData();
void SetFilter([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Interface)] object pFilter);
}
[ComImport, Guid("43826D1E-E718-42EE-BC55-A1E261C37BFE"), InterfaceType(ComInterfaceType.InterfaceIsIUnknown)]
internal interface IShellItem
{
void BindToHandler(IntPtr pbc, [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStruct)] Guid bhid, [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPStruct)] Guid riid, out IntPtr ppv);
void GetParent(out IShellItem ppsi);
[PreserveSig]
int GetDisplayName([In] SIGDN sigdnName, out IntPtr ppszName);
void GetAttributes([In] uint sfgaoMask, out uint psfgaoAttribs);
void Compare(IShellItem psi, uint hint, out int piOrder);
}
internal enum SIGDN : uint
{
SIGDN_FILESYSPATH = 0x80058000
}
[Flags]
internal enum FOS : uint
{
FOS_PICKFOLDERS = 0x20,
FOS_FORCEFILESYSTEM = 0x40
}
"@
# Check if the type is already loaded to avoid errors on repeated calls
if (-not ("FolderSelectDialog" -as [type])) {
Add-Type -TypeDefinition $code -ReferencedAssemblies System.Windows.Forms
}
$dialog = New-Object FolderSelectDialog
$dialog.Title = $Title
if ($dialog.ShowDialog()) {
return $dialog.FileName
}
return $null
}
# Conversion functions
function Convert-ExcelToPdf {
param($sourcePath, $destinationPath)
$excel = $null
try {
$excel = New-Object -ComObject Excel.Application
$excel.Visible = $false
$workbook = $excel.Workbooks.Open($sourcePath)
$workbook.ExportAsFixedFormat(0, $destinationPath) # 0 = xlTypePDF
$workbook.Close($false)
}
finally {
if ($excel) {
$excel.Quit()
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($excel) | Out-Null
}
}
}
function Convert-WordToPdf {
param($sourcePath, $destinationPath)
$word = $null
try {
$word = New-Object -ComObject Word.Application
$word.Visible = $false
$document = $word.Documents.Open($sourcePath)
$document.SaveAs($destinationPath, 17) # 17 = wdFormatPDF
$document.Close($false)
}
finally {
if ($word) {
$word.Quit()
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($word) | Out-Null
}
}
}
function Convert-PowerPointToPdf {
param($sourcePath, $destinationPath)
$powerpoint = $null
try {
$powerpoint = New-Object -ComObject PowerPoint.Application
$presentation = $powerpoint.Presentations.Open($sourcePath, $true, $false, $false) # ReadOnly, Untitled, WithWindow
$presentation.SaveAs($destinationPath, 32) # 32 = ppSaveAsPDF
$presentation.Close()
}
finally {
if ($powerpoint) {
$powerpoint.Quit()
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($powerpoint) | Out-Null
}
}
}
# Click events for browse buttons
$BrowseInputFolderButton.Add_Click({
$selectedPath = Select-FolderDialog -Title "Select Input Folder"
if (-not [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($selectedPath)) { $InputFolderPath.Text = $selectedPath }
})
$BrowseOutputFolderButton.Add_Click({
$selectedPath = Select-FolderDialog -Title "Select Output Folder"
if (-not [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($selectedPath)) { $OutputFolderPath.Text = $selectedPath }
})
# Click event for the execute button
$ExecuteButton.Add_Click({
$inputDir = $InputFolderPath.Text
$outputDir = $OutputFolderPath.Text
if (-not [System.IO.Directory]::Exists($inputDir) -or -not [System.IO.Directory]::Exists($outputDir)) {
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show("Please specify both input and output folders correctly.", "Error", "OK", "Error")
return
}
$ExecuteButton.IsEnabled = $false
$StatusText.Text = "Creating file list..."
$Window.Dispatcher.Invoke([System.Action]{}, [System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority]::Background) # Process UI events
$targetExtensions = @("*.xlsx", "*.xls", "*.docx", "*.doc", "*.pptx", "*.ppt")
$files = Get-ChildItem -Path $inputDir -Include $targetExtensions -Recurse
if ($files.Count -eq 0) {
$StatusText.Text = "No target files found."
$ExecuteButton.IsEnabled = $true
return
}
$ProgressBar.Minimum = 0
$ProgressBar.Maximum = $files.Count
$ProgressBar.Value = 0
$errors = [System.Collections.ArrayList]@()
$fileCount = 0
foreach ($file in $files) {
$fileCount++
$ProgressBar.Value = $fileCount
$StatusText.Text = "Processing: $($file.Name) ($fileCount/$($files.Count))"
$Window.Dispatcher.Invoke([System.Action]{}, [System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority]::Background) # Process UI events
$fileNameWithoutExt = [System.IO.Path]::GetFileNameWithoutExtension($file.Name)
$destinationPath = Join-Path $outputDir "$($fileNameWithoutExt).pdf"
try {
switch ($file.Extension.ToLower()) {
".xlsx" { Convert-ExcelToPdf -sourcePath $file.FullName -destinationPath $destinationPath }
".xls" { Convert-ExcelToPdf -sourcePath $file.FullName -destinationPath $destinationPath }
".docx" { Convert-WordToPdf -sourcePath $file.FullName -destinationPath $destinationPath }
".doc" { Convert-WordToPdf -sourcePath $file.FullName -destinationPath $destinationPath }
".pptx" { Convert-PowerPointToPdf -sourcePath $file.FullName -destinationPath $destinationPath }
".ppt" { Convert-PowerPointToPdf -sourcePath $file.FullName -destinationPath $destinationPath }
}
}
catch {
$errorMessage = "Failed to convert file '$($file.Name)': $($_.Exception.Message)"
$errors.Add($errorMessage) | Out-Null
}
}
if ($errors.Count -gt 0) {
$errorMessageText = "An error occurred with some files:`n`n" + ($errors -join "`n")
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show($errorMessageText, "Conversion Error", "OK", "Error")
$StatusText.Text = "An error occurred. Please check the message box for details."
} else {
$StatusText.Text = "Processing completed successfully."
}
$ExecuteButton.IsEnabled = $true
})
# Show the window
$Window.ShowDialog() | Out-Null
まとめ
今回は、Windows標準のPowerShellを活用して、日々の面倒な作業を効率化するGUIツールを作成しました。
環境構築の手間が不要なPowerShellは、特に企業内でツールを展開する際に非常に強力な選択肢となります。この記事が、皆さんの業務改善のヒントになれば幸いです。


コメント